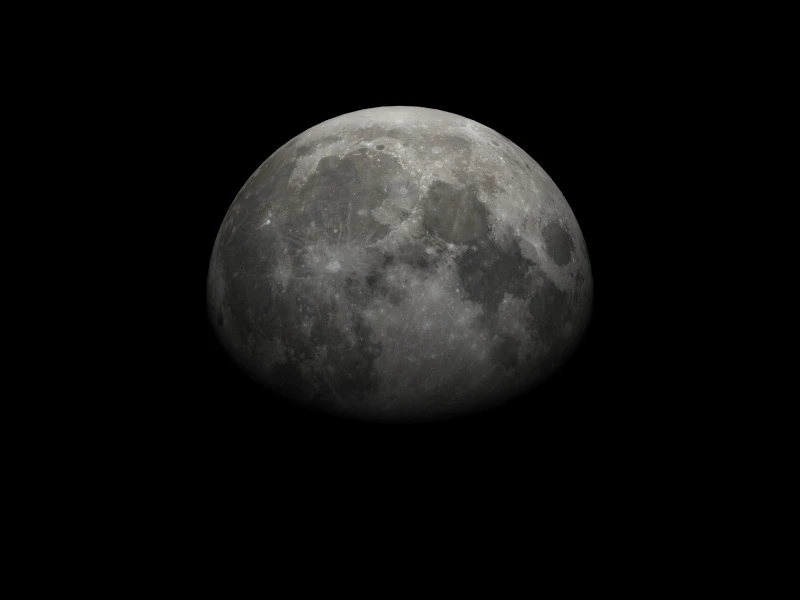
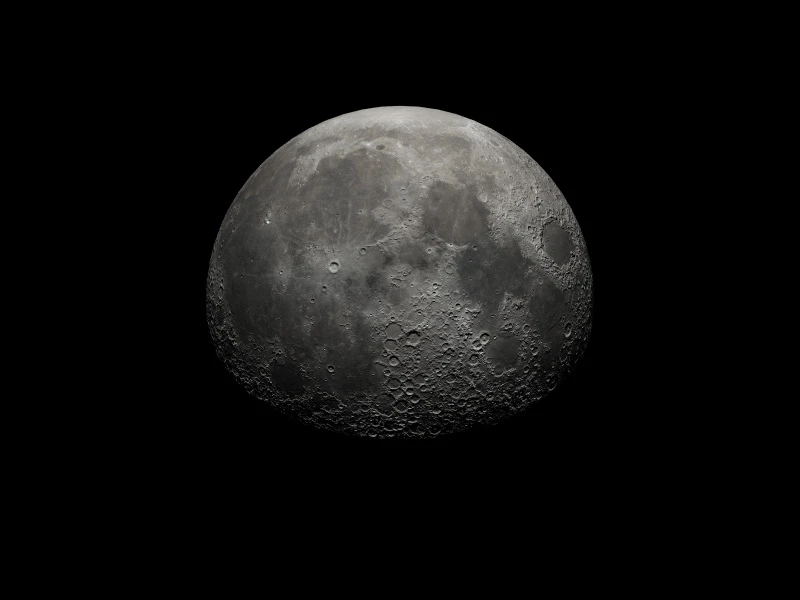
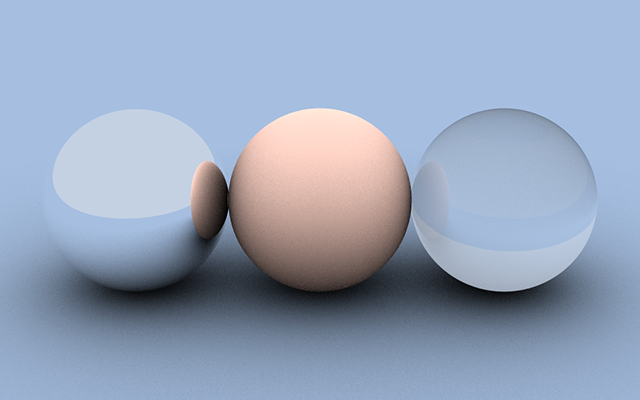
Features
Distribution Ray Tracing
Realistic simulation of light transport with support for reflections and shadows.
Global Illumination
Accurate rendering of indirect lighting effects for photorealistic images.
Cross-Platform
Compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux using C++17 and OpenCV.
Anti-aliasing
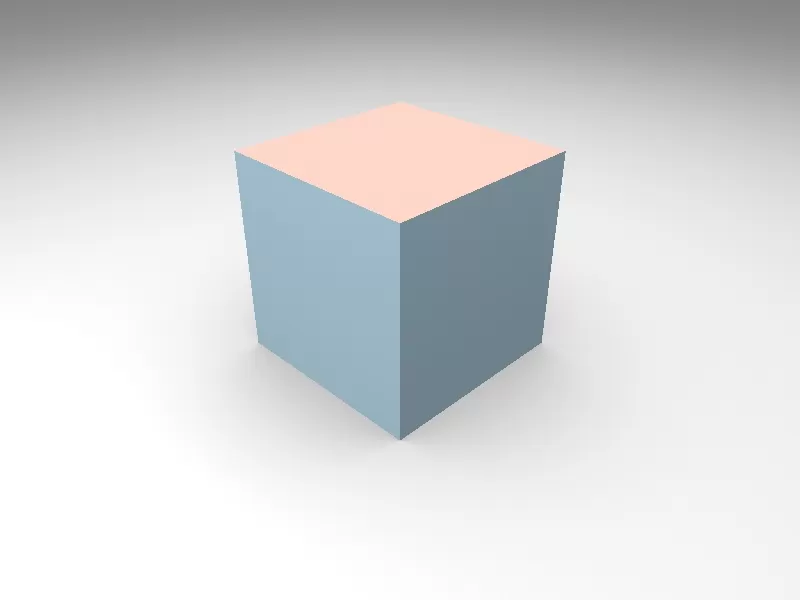
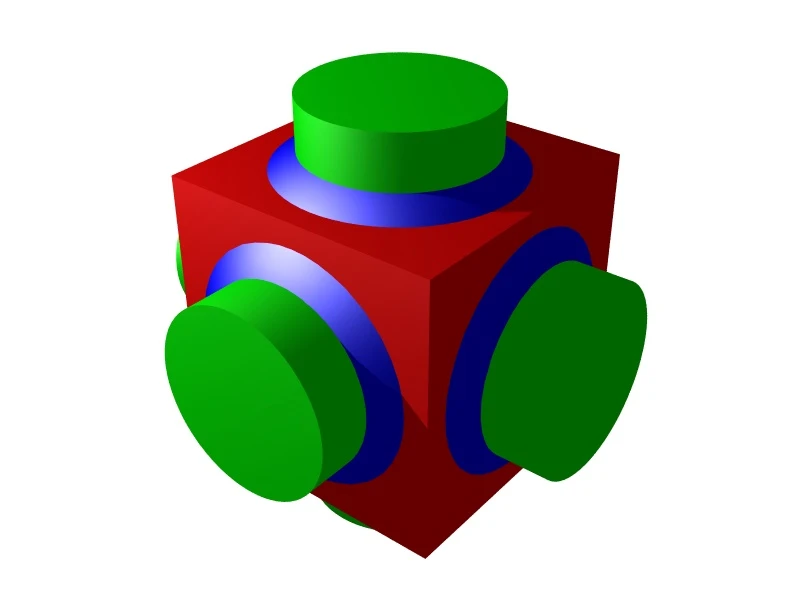
Constructive solid geometry (by Otmane Sabir)
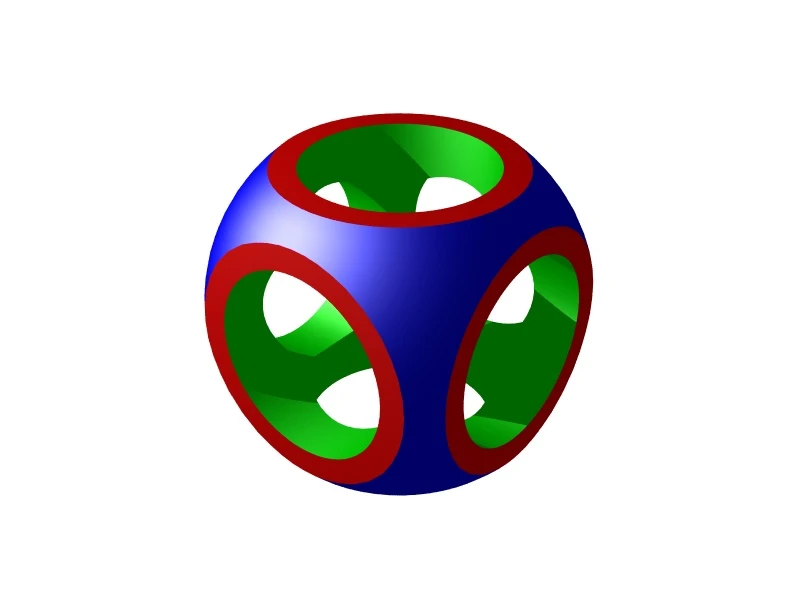
Area Lights
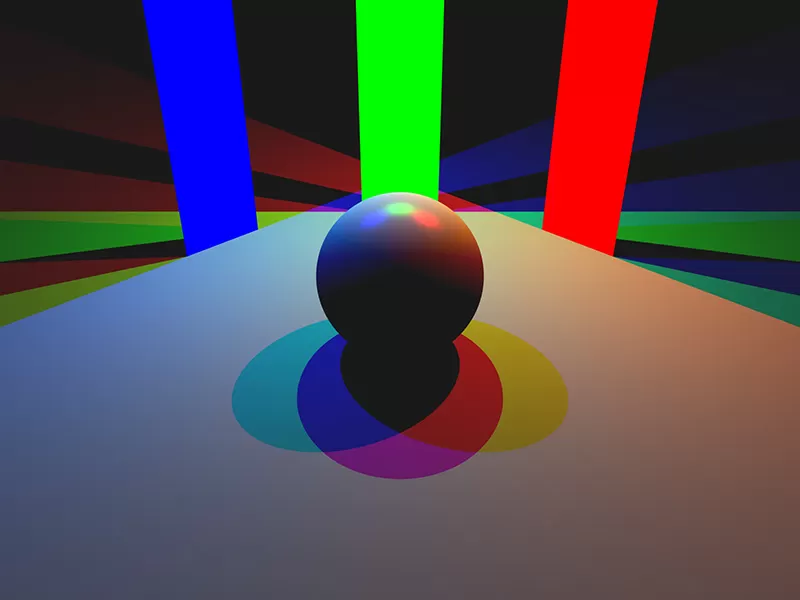
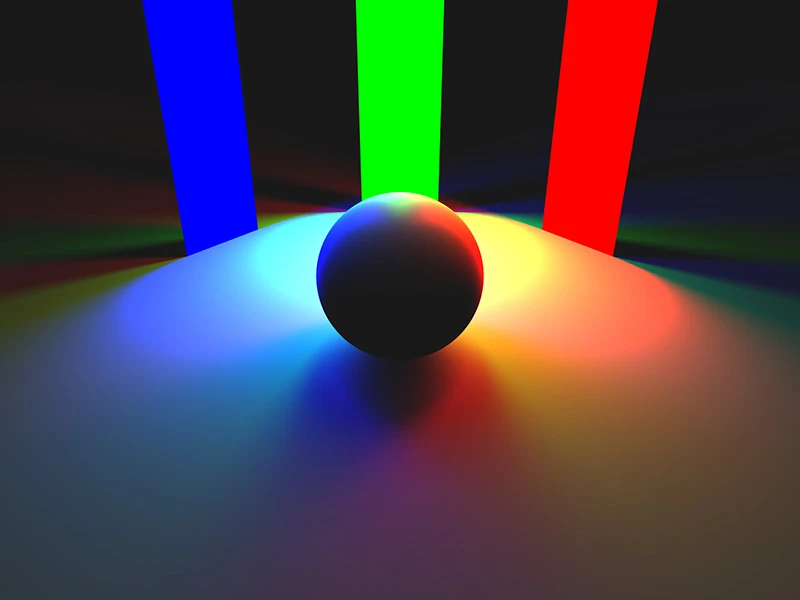


Ambient Occlusion
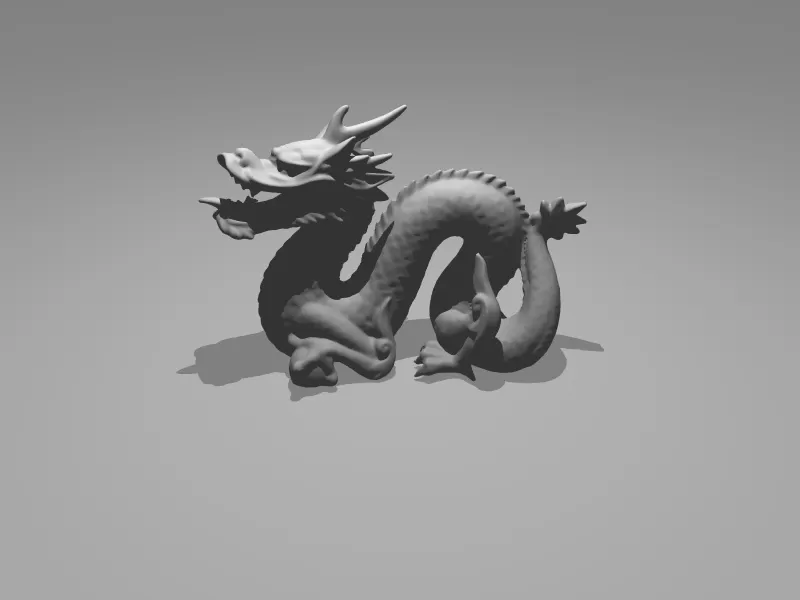
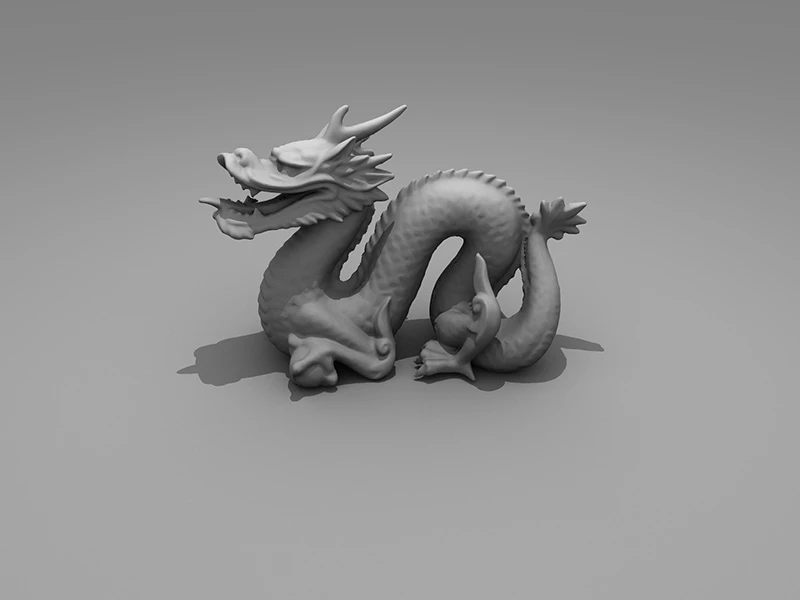


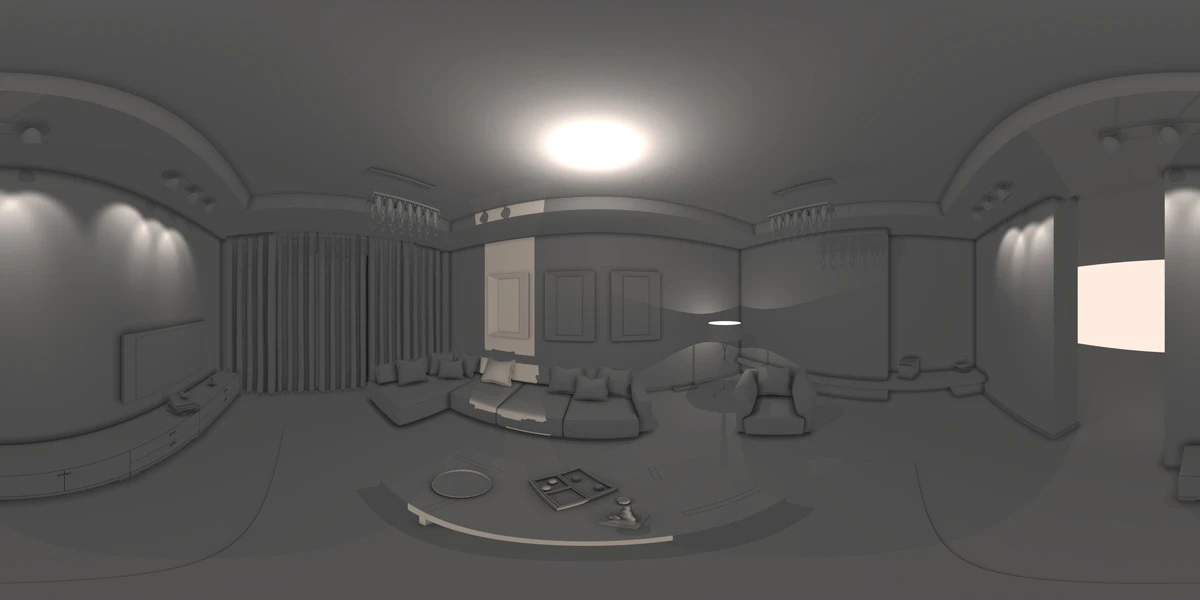
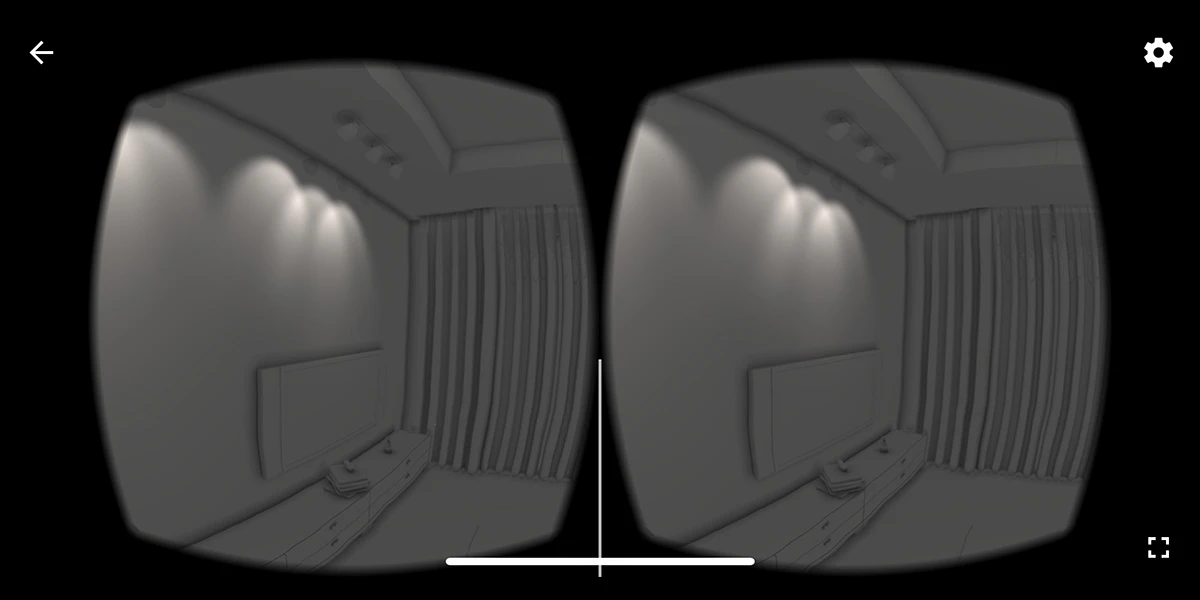
VR 360° Camera (by Fjolla Dedaj)

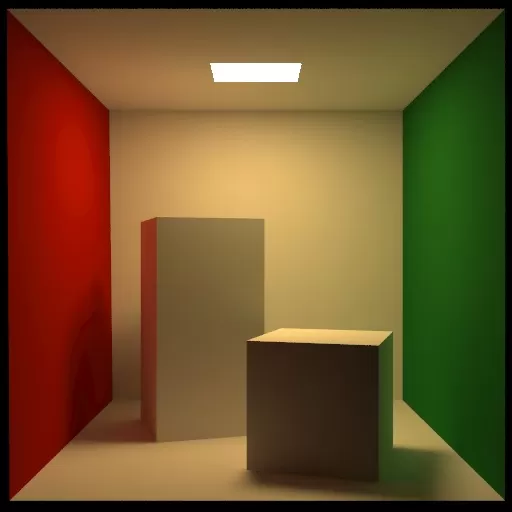
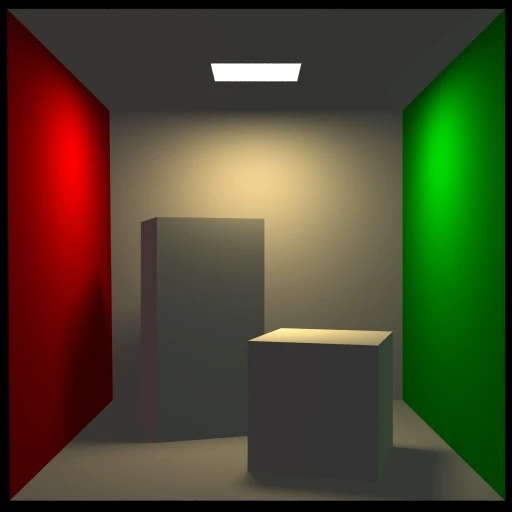
Cornell Box

Bump Mapping